
Robotic Surgery
- Metropolitan Hospital Nairobi, in partnership with Marengo Asia Hospitals (India), performs first robotic-assisted knee replacement surgeries in East and Central Africa;
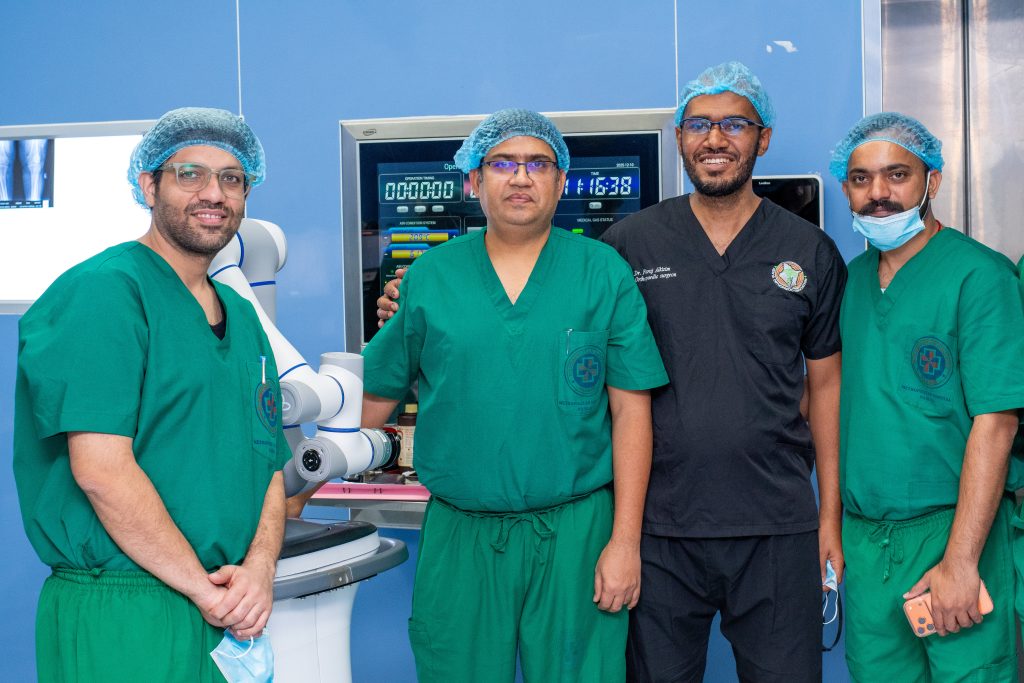
Metropolitan Hospital, Nairobi, in a clinical partnership with Marengo Asia Hospitals of India, has successfully performed the first robotic-assisted knee replacement surgeries in East and Central Africa, completing the inaugural procedures on 10 December 2025 at its facility.

The surgeries were conducted under a structured skills-transfer and clinical governance collaboration between Metropolitan and Marengo Asia Hospitals, aimed at strengthening local capacity for precision-based orthopaedic surgery and expanding access to advanced joint replacement care within the region.
The procedures were performed by orthopaedic surgeons from Metropolitan Hospital and Marengo Asia Hospitals.
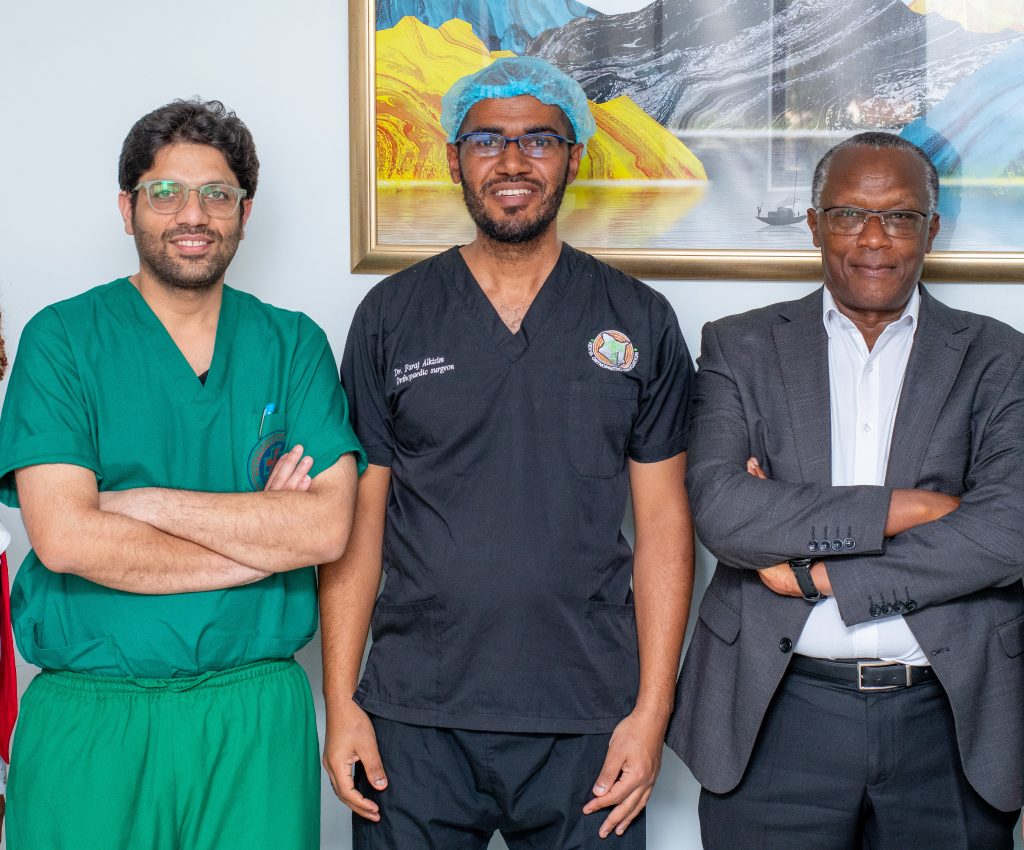
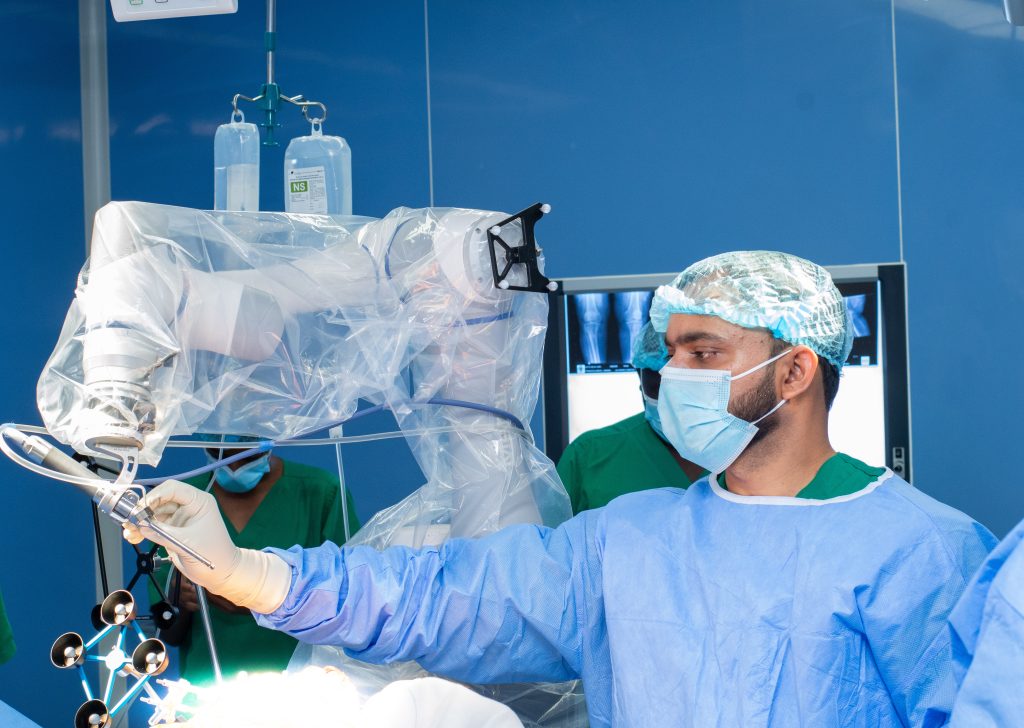 The inaugural case was led by Metropolitan’s Dr. Faraj Alkizim, alongside Marengo Asia Hospitals’ specialists Dr. Anurag Aggarwal and Dr. Rohit Thakkar.
The inaugural case was led by Metropolitan’s Dr. Faraj Alkizim, alongside Marengo Asia Hospitals’ specialists Dr. Anurag Aggarwal and Dr. Rohit Thakkar.
A second procedure was performed by Metropolitan’s Dr. Nathan Khamala, supported by the same specialist team.
All procedures were undertaken in line with established clinical protocols, applicable regulatory requirements and documented patient consent processes. Dr Kanyenje Gakombe, Founder and CEO of Metropolitan Hospital, said, “The introduction of robotic-assisted surgery at Metropolitan Hospital expands access to high-precision orthopaedic care in Kenya and the wider East and Central African region.
Dr Kanyenje Gakombe, Founder and CEO of Metropolitan Hospital, said, “The introduction of robotic-assisted surgery at Metropolitan Hospital expands access to high-precision orthopaedic care in Kenya and the wider East and Central African region.
It is the result of more than 30 years of investment in clinical training, infrastructure, and medical technology to ensure complex procedures can be delivered safely and consistently.
We believe strong partnerships and continuous innovation are essential to building local capacity in specialised care.
 This programme reflects that approach.” Knee replacement surgery is usually considered when the knee joint has been badly damaged and everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs or standing up become painful or difficult.
This programme reflects that approach.” Knee replacement surgery is usually considered when the knee joint has been badly damaged and everyday activities such as walking, climbing stairs or standing up become painful or difficult.
This damage can result from several causes, including long-term wear and tear, serious injuries from accidents, sports-related trauma, previous fractures or inflammatory joint diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
 Among these, osteoarthritis, a degenerative condition in which the cartilage that cushions the joint gradually wears away over time is the most common reason patients eventually require knee replacement.
Among these, osteoarthritis, a degenerative condition in which the cartilage that cushions the joint gradually wears away over time is the most common reason patients eventually require knee replacement.
Demand for joint replacement is rising globally as populations age and the burden of musculoskeletal conditions grows.
In Kenya, a 2024 peer-reviewed community study published in the Pan African Medical Journal among adults aged 40 years and above in rural Nyamira County reported an arthritis prevalence of 44.6%, underscoring the importance of strengthening local orthopaedic capacity.
 “Osteoarthritis is a significant contributor to disability globally and demand for joint replacement is
“Osteoarthritis is a significant contributor to disability globally and demand for joint replacement is
rising as populations age,” said Dr Faraj Alkizim, Orthopaedic Surgeon at Metropolitan Hospital.
“Robotic-assisted knee replacement is designed to support surgeons with patient-specific planning
and precise bone preparation, improving the accuracy of alignment and component positioning,
helping patients access advanced orthopaedic care closer to home.”
 According to the Ministry of Health (MoH), Kenya continues to face the challenge of large numbers of Kenyans seeking specialised treatment abroad, reinforcing the importance of building local centres of excellence and regional referral capability.
According to the Ministry of Health (MoH), Kenya continues to face the challenge of large numbers of Kenyans seeking specialised treatment abroad, reinforcing the importance of building local centres of excellence and regional referral capability.
Before the introduction of robotic-assisted surgery, an established arthroplasty service at Metropolitan Hospital was documented in a 2025 peer-reviewed study published in the Journal of Health, Medicine and Nursing, which followed 75 total knee replacement patients and reported that the hospital performed more than 140 total knee replacement procedures between January and May 2023.
Dr Raajiv Singhal, Founding Member, Group Managing Director and CEO, Marengo Asia Hospitals, India, said: “This collaboration reflects our approach of ‘Teach,Train, and Treat’, working closely with local surgical teams to embed global standards of planning, execution and governance into practice.
Our objective is to help reduce the need for patients to travel across borders for advanced treatment.”
The robotic system used in the procedures was supplied by Meril Life Sciences.Partners supporting
the programme include Meril Life Sciences, Wessex Pharmaceuticals and KCB.
 Metropolitan Hospital and Marengo Asia Hospitals will continue the clinical partnership to expand training, strengthen governance and scale access to advanced orthopaedic care, including additional robotic-assisted procedures and ongoing capacity-building for local surgical teams.
Metropolitan Hospital and Marengo Asia Hospitals will continue the clinical partnership to expand training, strengthen governance and scale access to advanced orthopaedic care, including additional robotic-assisted procedures and ongoing capacity-building for local surgical teams.







